Copernicus solar system theory
 The Copernican Planisphere, illustrated in 1661 by Andreas Cellarius.
The Copernican Planisphere, illustrated in 1661 by Andreas Cellarius.
Credit: Public domain
In the early 1500s, when virtually everyone believed Earth was the center of the universe, Polish scientist Nicolaus Copernicus proposed that the planets instead revolved around the sun. Although his model wasn't completely correct, it formed a strong foundation for future scientists to build on and improve mankind's understanding of the motion of heavenly bodies.
Indeed, other astronomers built on Copernicus’ work and proved that our planet is just one world orbiting one star in a vast cosmos loaded with both, and that we’re far from the center of anything.
[See also our overview of and great scientists from many fields who have contributed to the rich history of discoveries in astronomy.]
Here is a brief biography of Copernicus:
Celestial education
Born on Feb. 19, 1473, in Poland, Copernicus traveled to Italy at the age of 18 to attend college, where he prepared for a career in the church. As part of his education, he studied astrology — reading the stars to learn about future events — because at the time it was felt important for priests and doctors. Astronomy, the motion of heavenly bodies, was an important element of this. (Today, astronomy is a recognized science, whereas astrology is not.)
Nicolaus Copernicus
Credit: Public Domain
While attending the University of Bologna, he lived and worked with astronomy professor Domenico Maria de Novara, doing research and helping him make observations of the heavens. When he returned to Poland to take up official duties in Frauenburg, his room in one of the towers surrounding the town boasted an observatory, giving him ample time and opportunity to study the night sky. Copernicus never took orders as a priest, but instead continued to work as a cleric.
A new model
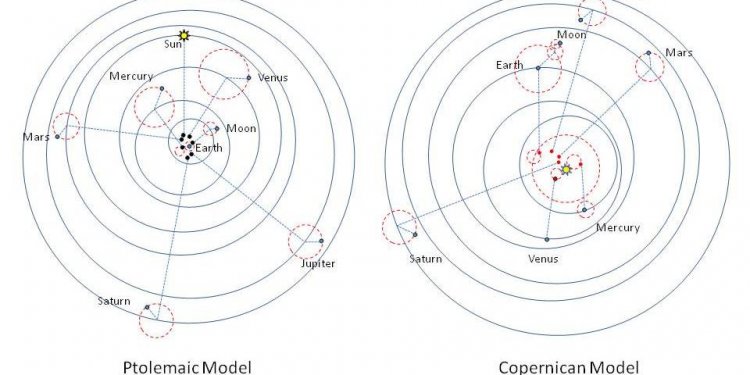
One of the glaring mathematical problems with this model was that the planets, on occasion, would travel backward across the sky over several nights of observation. Astronomers called this retrograde motion. To account for it, the current model, based on the Greek astronomer and mathematician Ptolemy's view, incorporated a number of circles within circles — epicycles — inside of a planet's path. Some planets required as many as seven circles, creating a cumbersome model many felt was too complicated to have naturally occurred.
 In 1514, Copernicus distributed a handwritten book to his friends that set out his view of the universe. In it, he proposed that the center of the universe was not Earth, but that the sun lay near it. He also suggested that Earth's rotation accounted for the rise and setting of the sun, the movement of the stars, and that the cycle of seasons was caused by Earth's revolutions around it. Finally, he (correctly) proposed that Earth's motion through space caused the retrograde motion of the planets across the night sky (planets sometimes move in the same directions as stars, slowly across the sky from night to night, but sometimes they move in the opposite, or retrograde, direction).
In 1514, Copernicus distributed a handwritten book to his friends that set out his view of the universe. In it, he proposed that the center of the universe was not Earth, but that the sun lay near it. He also suggested that Earth's rotation accounted for the rise and setting of the sun, the movement of the stars, and that the cycle of seasons was caused by Earth's revolutions around it. Finally, he (correctly) proposed that Earth's motion through space caused the retrograde motion of the planets across the night sky (planets sometimes move in the same directions as stars, slowly across the sky from night to night, but sometimes they move in the opposite, or retrograde, direction).
It wasn't until he lay on his deathbed at the age of 70 that Copernicus published his book, De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium ("On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres"). In it, Copernicus established that the planets orbited the sun rather than the Earth. He lay out his model of the solar system and the path of the planets.
Refining the work
Although Copernicus' model changed the layout of the universe, it still had its faults. For one thing, Copernicus held to the classical idea that the planets traveled in perfect circles. It wasn't until the 1600s that Johannes Kepler proposed the orbits were instead ellipses. As such, Copernicus' model featured the same epicycles that marred in Ptolemy's work, although there were fewer.
Copernicus' ideas, published only two months before he died, took nearly a hundred years to seriously take hold. When Galileo Galilei claimed in 1632 that Earth orbited the sun, building upon the Polish astronomer's work, he found himself under house arrest for committing heresy against the Catholic church.
Despite this, the observations of the universe proved the two men correct in their understanding of the motion of celestial bodies. Today, we call the model of the solar system, in which the planets orbit the sun, a heliocentric or Copernican model.