Stellar Habitable Zones
Habitable zone the orbital region around a in which an -like can possess liquid on its surface and possibly support life. Liquid water is essential to all on , and so the definition of a habitable zone is based on the hypothesis that would share this requirement. This is a very conservative (but observationally useful) definition, as a planet’s surface temperature depends not only on its proximity to its but also on such factors as its atmospheric , its reflectivity, and its atmospheric or oceanic circulation. Moreover, internal energy sources such as radioactive decay and tidal heating can warm a planet’s surface to the melting point of water. These energy sources can also maintain subsurface reservoirs of liquid water, so a could contain life without being within its star’s habitable zone. Earth, for instance, has a thriving subsurface , albeit one that is composed almost exclusively of simple organisms that can survive in -poor environments. ’s has a liquid water ocean tens of kilometres below its surface that may well be habitable for some organisms.
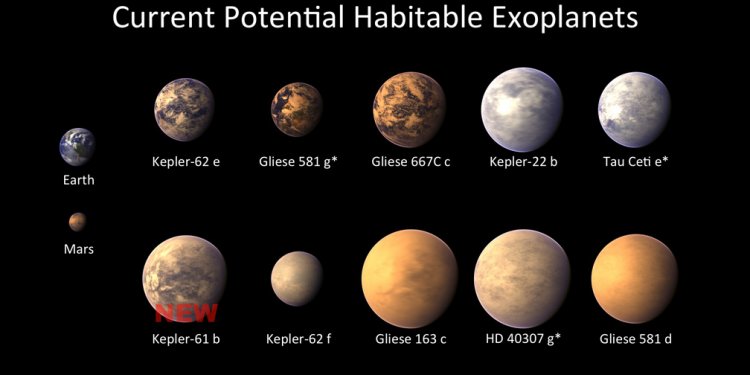
More than 20 planets, including the nearest , b, have been found that are both roughly Earth-sized and orbiting within the habitable zones of their stars. Astronomers have also used simulations of the climates of other extrasolar planets such as to determine that they could have surface water under the right climatic conditions.
Boundaries
The inner boundary of a habitable zone is where water would be lost as a result of a runaway , in which greenhouse gases in a planet’s atmosphere would trap incoming , leading to the planet’s becoming hotter and hotter until the water boiled away. The outer boundary is where such greenhouse warming would not be able to maintain surface temperatures above freezing anywhere on the planet. Astronomers have calculated the extent of the habitable zone for many different types of stars. For example, at present, the habitable zone of the is estimated to extend from about 0.9 to 1.5 s (the distance between Earth and the Sun).
The location of a star’s habitable zone depends upon its . Because a star’s luminosity increases with time, both the inner and outer boundaries of its habitable zone move outward. Thus, a planet that is in the habitable zone when a star is young may subsequently become too hot. may have been such a planet; however, because it is geologically active, its current surface is too young to show any evidence that a more clement climate may have existed billions of years ago. Other planets could be too cold for liquid water to exist when their star is young but might warm up enough to have liquid water on their surface later as their star’s luminosity increases. This may happen to a few billion years hence. Thus, the most promising region to find Earth-like life would be in a “continuously habitable zone, ” where liquid water could have been present from early in the star’s life up to the current epoch. The continuously habitable zone of the Sun (from four billion years ago to the present) is from about 0.9 to 1.2 astronomical units.
Changes in the Sun’s habitable zone
Test Your Knowledge

Astronomy and Space Quiz
Earth has had liquid water on its surface for much of the past four billion years. However, four billion years ago the Sun’s luminosity was only about 75 percent as intense as it is at present, and climate models suggest that Earth should have been frozen over at such a low solar luminosity. This apparent disagreement between theory and observation is known as the “faint young Sun problem.” Another planet to which the faint young Sun problem might apply is Mars. On that planet the oldest regions of the surface show signs of running water while younger regions do not, which suggests that Mars had a warmer and thicker atmosphere in the past, when the Sun was less luminous, than it has now that the Sun is brighter. The warmth of Earth and Mars during their early periods (and thus the solution to the faint young Sun problem) can be attributed to the presence of abundant greenhouse gases in their atmospheres, with , water, and possibly and playing major roles.